Change Management in Safety: What You Need to Know
Change is inevitable. But in safety management, it’s how you manage change that truly matters. Every tweak, whether it’s a new piece of equipment, a process update, or a shift in personnel, can introduce new risks. This is where Change Management, or Management of Change (MOC), comes into play.
It’s the process that ensures changes don’t compromise safety, acting as a safety net that catches risks before they become real problems.
Why MOC is Essential
When a new process, material, or even personnel is introduced, it can disrupt established safety protocols. These disruptions can lead to new hazards or exacerbate existing ones. Without a structured approach to managing these changes, the likelihood of incidents increases significantly.
MOC helps maintain control over the safety environment, ensuring that every change is assessed, approved, and implemented with safety as the top priority. It’s about being proactive rather than reactive—anticipating potential risks and addressing them before they escalate.
Moreover, MOC is essential because it promotes a culture of continuous safety improvement. By regularly assessing and managing changes, organizations can evolve their safety practices, making them more resilient and robust over time.
Key Steps in the MOC Process
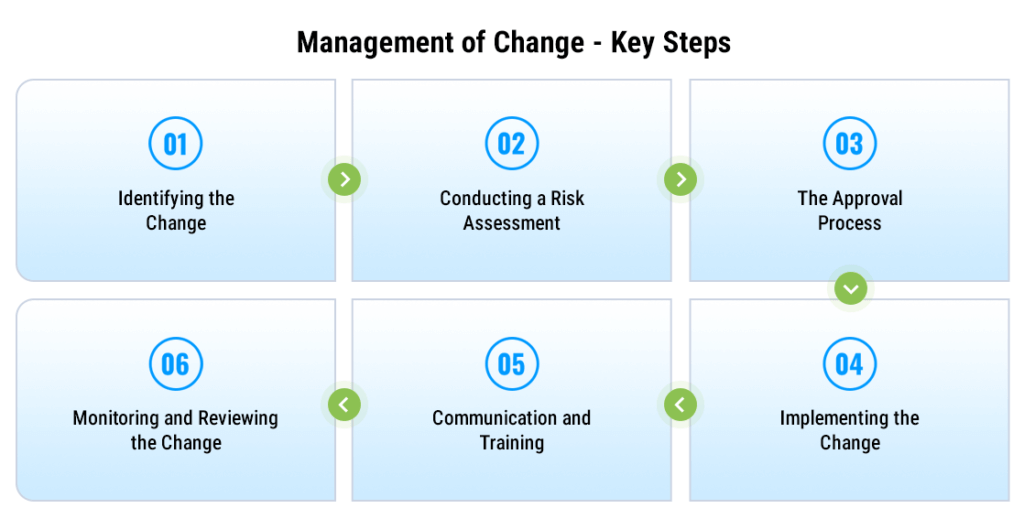
1. Identifying the Change:
The first step is spotting the change. It might seem obvious, but not all changes are immediately recognized. Sometimes, what appears to be a minor adjustment can have significant safety implications. Recognizing when a change needs to be managed is the foundation of effective MOC.
2. Conducting a Risk Assessment:
Once a change is identified, the next step is to assess the risks. This involves asking the right questions. What new hazards could this change introduce? How could it impact existing safety measures? A thorough risk assessment helps in understanding the potential dangers and how to mitigate them.
3. The Approval Process:
No change should occur without proper approval. This step ensures that every change is reviewed by the right people. It’s about having a second pair of eyes, or even a third, to spot anything that might have been missed. It’s a checkpoint that safeguards the entire process.
4. Implementing the Change:
With approval in hand, the change can be implemented. But this isn’t just about making the switch. It’s about doing it safely. Following safety protocols during implementation is crucial to ensure that the change doesn’t introduce new risks.
5. Communication and Training:
A change can only be safe if everyone involved knows about it. That’s why communication is key. All affected personnel need to be informed, and in many cases, trained on how the change impacts their work. Clear communication prevents misunderstandings that could lead to accidents.
6. Monitoring and Reviewing the Change:
Even after a change is implemented, the work isn’t done. Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the change doesn’t lead to unexpected issues. Reviewing the change after some time allows for adjustments if necessary, ensuring long-term safety.
Overcoming Common Challenges in MOC
Managing change is rarely straightforward. There are common challenges that can derail the process. Resistance from employees, for example, is a typical hurdle. People are often wary of change, especially when it feels like more work or introduces uncertainty.
How to Overcome Resistance:
- Involve Employees Early: Get them involved from the start. When people feel they have a say in the process, they’re more likely to support it.
- Communicate Clearly: Explain why the change is necessary. Show how it benefits everyone in the long run.
Addressing Communication Breakdowns:
- Use Multiple Channels: Don’t rely on just one method of communication. Use emails, meetings, and even informal conversations to get the message across.
- Follow Up: Ensure that everyone has understood the change. Ask questions, gather feedback, and be ready to clarify any doubts.
Best Practices for Effective MOC
1. Regular Audits:
Keep your MOC process under regular review. Audits can help spot weaknesses and areas for improvement. They also provide an opportunity to update processes in line with the latest safety standards and regulations.
2. Cross-Functional Teams:
Involve people from different departments. A diverse team brings different perspectives, ensuring all angles are covered. This approach not only enhances the thoroughness of the MOC process but also promotes collaboration and shared responsibility across the organization.
3. Continuous Improvement:
MOC isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it process. Learn from each change, and make adjustments to improve future implementations. Regularly refining the MOC process ensures that it remains effective and adaptable to evolving safety challenges.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.