15 Key Safety Metrics You Need To Track
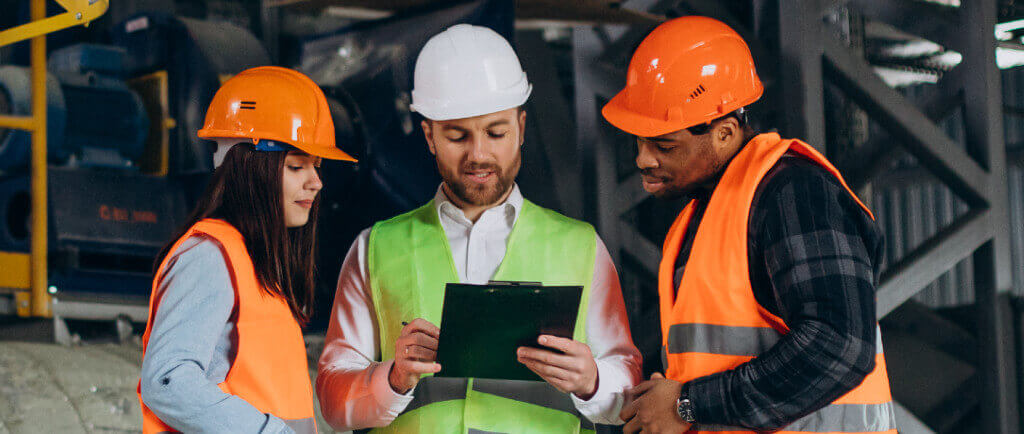
Ensuring workplace safety requires tracking and monitoring various key safety metrics to identify potential hazards, assess the effectiveness of safety measures, and prevent accidents or injuries.
In this article, we’ll explore 15 critical safety metrics that every workplace should monitor, shedding light on how these metrics not only protect employees but also contribute to the overall success of the organization.
The 15 key safety metrics are:
- Incident rate
- Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR)
- Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR)
- Near miss reporting rate
- Severity rate
- Safety training completion rate
- Safety compliance audit results
- Safety perception surveys
- Equipment maintenance and inspection records
- Emergency response time
- First aid kit usage
- Safety committee meeting attendance
- Workplace ergonomics assessments
- Incident investigation closure rate
- Safety leading indicators
Let’s now look closer at each of these metrics and understand how they contribute towards workplace safety.
1. Incident Rate:
The incident rate measures the number of workplace incidents (injuries, illnesses, near misses, and accidents) per a specific unit of time or number of hours worked. It helps to assess the overall safety performance and identify trends.
The incident rate, reflecting workplace incidents per hours worked, is a vital safety metric. It gauges the effectiveness of safety measures and spots potential hazards. A high rate may necessitate improved training or procedures, while a decreasing rate signals safety progress. Regular monitoring of incident rates through a safety dashboard can help organizations prevent accidents and prioritize safety.
Related read: Our listing of the best Health and Safety Software.
2. Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR):
The Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR) calculates the number of work-related injuries resulting in lost workdays per 100 full-time employees. It’s a critical metric for measuring the severity of injuries and their impact on productivity.
LTIR serves as an essential safety gauge, highlighting the impact of injuries on workforce productivity. Organizations rely on LTIR to pinpoint areas for improvement, such as enhanced training or safer procedures, and to track their journey toward a safer workplace.
3. Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR):
Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) encompasses all work-related injuries, illnesses, and fatalities that require medical treatment or result in lost workdays. It offers a comprehensive view of workplace safety incidents and helps organizations assess their overall safety performance.
TRIR provides a holistic perspective on workplace safety by considering all types of incidents. This metric is invaluable for organizations striving to reduce injuries, illnesses, and fatalities, guiding them toward a safer work environment.
Related: TRIR Calculator
4. Near Miss Reporting Rate:
Encouraging employees to report near misses, incidents narrowly avoided, is vital. Monitoring the rate of near miss reporting fosters a proactive safety culture, allowing organizations to identify potential hazards before they lead to actual incidents.
Near Miss Reporting Rate sheds light on close calls that could have resulted in injuries or accidents. It’s a crucial metric for nurturing a culture of prevention and continuous improvement, making workplaces safer by addressing risks proactively.
Learn more about the Safetymint near miss reporting software.
5. Severity Rate:
The Severity Rate quantifies the gravity of workplace incidents, assigning numerical values to different types of injuries and illnesses. This helps organizations prioritize safety efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Severity Rate categorizes incidents based on severity, enabling organizations to target resources and interventions where they are most needed. By focusing on the severity of incidents, organizations can work toward reducing the impact of workplace accidents.
6. Safety Training Completion Rate:
Ensuring employees complete required safety training is essential. Tracking the percentage of employees who have completed these programs is crucial for assessing compliance and reducing workplace risks.
Safety Training Completion Rate ensures that employees receive necessary safety training, minimizing the likelihood of accidents resulting from inadequate training or awareness. It’s a cornerstone of a safety-conscious workplace.
7. Safety Compliance Audit Results:
Regular safety audits assess compliance with safety regulations and policies. Monitoring the results of these audits ensures that safety standards are upheld and areas in need of improvement are identified.
Safety Compliance Audit Results are instrumental in ensuring adherence to safety protocols. They provide insights into areas requiring attention and allow organizations to rectify non-compliance promptly.
8. Safety Perception Surveys:
Surveys gauge employees’ perception of safety in the workplace. This qualitative data offers insights into communication, equipment maintenance, or training issues that may require attention.
Safety Perception Surveys tap into the collective wisdom of employees, revealing aspects of safety culture that may not be apparent through quantitative metrics alone. They empower organizations to address nuanced safety concerns effectively.
9. Equipment Maintenance and Inspection Records:
Maintaining records of equipment maintenance and inspections ensures that machinery and safety systems are regularly reviewed, reducing the risk of accidents.
Equipment Maintenance and Inspection Records play a pivotal role in proactive risk management. By documenting maintenance and inspections, organizations keep their equipment in optimal condition, minimizing the chance of safety-related incidents.
10. Emergency Response Time:
Tracking the response time of emergency services or internal response teams is crucial in minimizing the impact of workplace accidents or emergencies.
Emergency Response Time is a key determinant of how effectively organizations can mitigate the consequences of accidents. It emphasizes the importance of swift action when safety incidents occur.
11. First Aid Kit Usage:
Monitoring the usage of first aid supplies provides insights into the frequency and types of injuries occurring in the workplace, aiding in better safety planning.
First Aid Kit Usage data serves as a practical indicator of workplace safety incidents. By assessing first aid kit utilization, organizations can tailor their safety measures to address specific injury types or frequency.
12. Safety Committee Meeting Attendance:
Tracking attendance and reviewing meeting minutes for safety committee meetings ensures that safety concerns are actively addressed by employees.
Safety Committee Meeting Attendance reflects employees’ engagement in safety discussions and decision-making. It reinforces the importance of collaboration in maintaining a safe workplace.

13. Workplace Ergonomics Assessments:
Conducting assessments of workplace ergonomics can help prevent musculoskeletal disorders and improve employee comfort, reducing potential health risks.
Workplace Ergonomics Assessments are proactive measures aimed at preventing injuries caused by poor ergonomic conditions. They demonstrate an organization’s commitment to employee well-being.
14. Incident Investigation Closure Rate:
Tracking the rate at which incident investigations are completed and corrective actions are implemented ensures that lessons are learned and improvements are made promptly.
Incident Investigation Closure Rate underscores the importance of not only investigating incidents but also swiftly implementing corrective actions. It reflects an organization’s commitment to continuous improvement in safety.
15. Safety Leading Indicators:
These proactive metrics, such as the number of safety suggestions implemented or safety inspections completed on time, predict future safety performance, helping organizations take preventive measures to enhance workplace safety.
Safety Leading Indicators provide foresight into safety performance, allowing organizations to take proactive steps to prevent incidents. They serve as early warning signs, guiding safety efforts to minimize risks.
Related read: leading and lagging indicators in safety.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.