Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) Explained
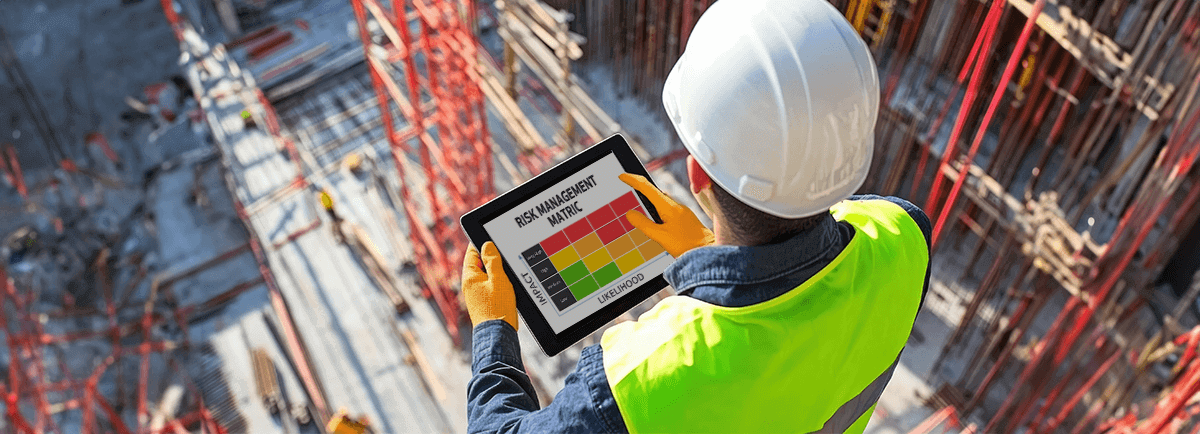
When it comes to safety and risk management, guessing isn’t an option. Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) provides a data-driven approach to evaluating risks, ensuring decisions are based on facts, not assumptions.
Unlike qualitative methods that rely on subjective judgments, QRA assigns measurable values to risks—helping organizations predict the likelihood and impact of hazardous events. Whether it’s preventing industrial accidents, mitigating chemical spills, or assessing explosion risks, QRA plays a vital role in protecting lives, assets, and the environment.
In this guide, we’ll break down what QRA is, its key components, how it works, and why it matters—all in a simple and practical way.
What is Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)?

Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) is a structured process used to identify, analyze, and quantify risks in numerical terms. It determines the probability of hazardous events occurring and their potential consequences, helping organizations make informed safety decisions.
QRA is widely used in high-risk industries like oil & gas, chemicals, and construction, where a single incident can have catastrophic consequences. It provides organizations with a clear understanding of risk levels and guides them in implementing necessary safety measures.
How QRA Differs from Qualitative Risk Assessment
- QRA uses data and probability models to quantify risks, while qualitative assessments rely on subjective categories (e.g., high, medium, or low risk).
- QRA calculates potential losses and fatalities, offering a precise evaluation rather than a general risk rating.
- It supports regulatory compliance and decision-making by providing clear, measurable risk thresholds.
Key Components of QRA
A QRA study typically involves four fundamental components, each playing a crucial role in risk evaluation.
1. Hazard Identification
The first step in any risk assessment is recognizing potential hazards. These could be flammable substances, toxic chemicals, equipment failures, or human errors. Organizations use structured techniques like HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study), FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis), or Bowtie Analysis to systematically pinpoint risks.
2. Frequency Analysis
Once hazards are identified, the next step is determining how often an event might occur. This involves analyzing historical accident data, failure rates of equipment, and operational conditions. Probability models and industry benchmarks help estimate the likelihood of different scenarios unfolding.

3. Consequence Analysis
Even if an incident occurs, its impact can vary—from minor operational disruptions to large-scale disasters. Consequence analysis evaluates the potential damage to people, property, and the environment. Fire, explosion, and toxic release scenarios are modeled using advanced simulation techniques to understand their worst-case outcomes.
4. Risk Estimation & Evaluation
Risk estimation combines frequency and consequence data to provide a measurable risk value. The organization then compares this value with predefined risk tolerance levels. If the risk is too high, control measures must be implemented to reduce exposure and improve workplace safety.
Steps in Conducting a QRA
A structured approach ensures a thorough and effective risk assessment. Here’s how QRA is typically conducted:
1. Define Objectives & Scope
Clearly outline what the assessment aims to achieve—whether it’s evaluating fire hazards, chemical leaks, or explosion risks. Defining the scope ensures that the assessment remains focused and relevant to the organization’s safety goals.
2. Identify Hazards
Using established methodologies like HAZOP, Bowtie Analysis, or FMEA, organizations identify potential hazards associated with operations, equipment, or external factors. The goal is to create a comprehensive list of possible risks.

3. Collect Data & Assess Frequency
Historical data, industry reports, and failure rate statistics are gathered to estimate how often hazardous events may occur. This step often involves probability calculations and past incident reviews.
4. Model Consequences
This step involves using simulation tools to predict what would happen if a hazard materialized. Fire spread, toxic gas dispersion, or explosion impact are analyzed to understand the potential severity of incidents.
5. Calculate Risk
Using the formula Risk = Probability × Consequence, organizations can assign a numerical value to each identified risk. This helps in prioritizing risk mitigation efforts based on which hazards pose the greatest threat.
6. Implement Control Measures
If the assessed risk exceeds acceptable levels, safety measures must be implemented. These could include engineering controls, protective barriers, process modifications, or emergency response plans to minimize potential consequences.
Benefits and Limitations of QRA
Benefits
- Data-Driven Decision-Making – Eliminates guesswork by providing measurable risk values.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet safety standards like OSHA, ISO 31000, and EPA guidelines.
- Cost Savings – Prevents accidents, reducing downtime, legal penalties, and insurance costs.
- Improved Emergency Preparedness – Enables organizations to plan responses for worst-case scenarios.
Limitations
- Data-Intensive – Requires accurate historical data for reliable risk calculations.
- Computational Complexity – Needs advanced tools and expertise for accurate modeling.
- Limited Consideration of Human Factors – May not fully account for human error and unpredictable behaviors.
- Expensive to Implement – Requires specialized software and trained professionals.
Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) is an essential tool for industries where safety is non-negotiable. By systematically identifying, analyzing, and quantifying risks, QRA helps organizations make better decisions, comply with safety regulations, and prevent catastrophic incidents.
While it requires expertise and accurate data, the benefits far outweigh the challenges—providing a structured approach to reducing risks and improving workplace safety.
Would you like to explore how digital solutions can simplify risk assessments? Let us know!
This article was generated with the assistance of AI and reviewed by Ramesh Nair for accuracy and quality.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.