Understanding the Safety Pyramid for Workplace Safety
Have you ever heard of the safety pyramid or Heinrich Triangle? It’s a game-changer in the world of workplace safety. Imagine a triangle that helps predict and prevent accidents. Sounds interesting, right?
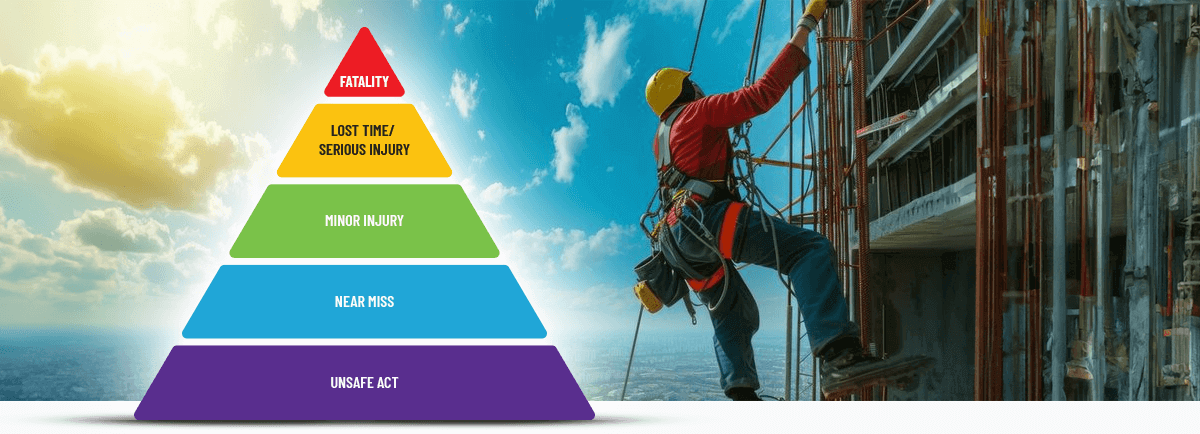
The concept dates back to the 1930s, thanks to Herbert William Heinrich, a pioneer in industrial safety. He discovered a fascinating pattern: for every major accident, there are 29 minor injuries and 300 near misses. Picture a pyramid with fatal accidents at the top, major injuries in the middle, and near misses forming the broad base. This structure isn’t just theoretical—it’s a practical tool for saving lives.
Why is the safety pyramid, also called the safety triangle, important? Think of it as a crystal ball for safety. By addressing minor incidents and near misses, we can prevent serious accidents. It’s all about being proactive, not reactive.
Let’s bring this to life with an example. Imagine a construction site where workers frequently trip over loose cables. These are the near misses at the pyramid’s base. If ignored, they could lead to minor injuries, like a twisted ankle. Worse still, these minor injuries could escalate to a major accident—a worker falling from a height.
In the next sections, we’ll dive deeper into how the safety pyramid works and how you can leverage it to create a safer, more productive work environment. Stay tuned!
The Structure of the Safety Pyramid
The safety pyramid is a simple yet powerful concept. Let’s breaks it down with an illustration:
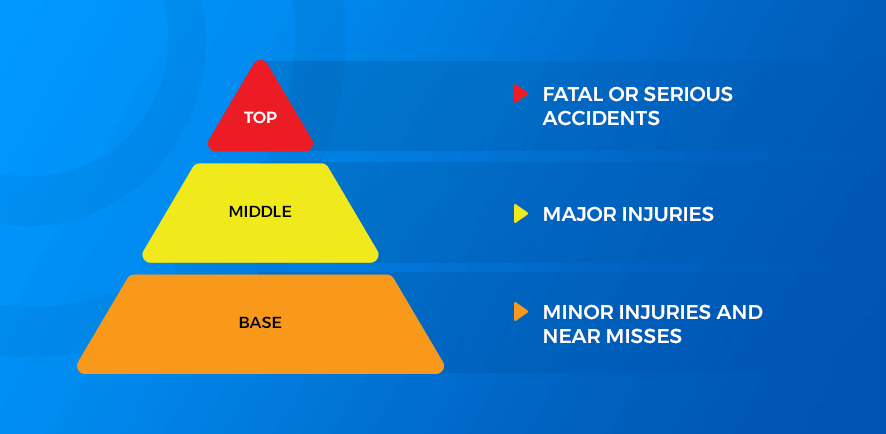
Each tier is a layer of protection. By focusing on the base, you prevent issues from climbing up the pyramid.
Think of the base as the foundation of a building. If the foundation is weak, the entire structure is at risk. The same goes for safety. Ignoring near misses and minor injuries can lead to serious accidents.
Predictive Power of the Safety Pyramid
The magic of the safety pyramid lies in its predictive power. Addressing small issues helps prevent bigger problems. It’s like fixing a small leak before it becomes a flood.
Consider a manufacturing plant where workers often slip on spilled oil. These slips are the near misses. If addressed promptly, they prevent minor injuries. If left unchecked, they can lead to serious falls and major accidents.
By using the safety pyramid, companies can identify patterns. They can see where most near misses occur and take steps to eliminate them. This proactive approach is key to maintaining a safe work environment.
Implementing the Safety Pyramid in Safety Programs
So, how do you implement the safety pyramid in your safety programs? Here are some steps:
1. Track Near Misses: Encourage employees to report near misses. Make it easy and anonymous if needed.
2. Analyze Data: Use tools like Safetymint to analyze incident data. Look for patterns and trends.
3. Take Action: Address the root causes of near misses. Fix hazards before they lead to injuries.
4. Educate Employees: Train your team on the importance of reporting and addressing near misses.
Safetymint’s Role in Enhancing Safety
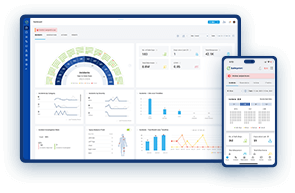
At Safetymint, we understand the importance of the safety pyramid. Our safety dashboard displays the pyramid prominently, offering a clear view of your safety performance.
Key Features of Safetymint:
Incident Reporting: Easily report near misses, minor injuries, and major accidents.
Data Analytics: Our statistics section provides in-depth analysis of incident data.
Custom Workflows: Create custom workflows to address specific safety needs.
Alerts and Notifications: Get notified when incidents are reported or actions are overdue.
Root Cause Analysis: Use our 5-step incident investigation process for thorough analysis.
These features help you leverage the safety pyramid to its full potential. By focusing on near misses and minor incidents, you can prevent major accidents and ensure a safer workplace.
Learn more about the Safetymint workplace safety software.

Ramesh Nair is the Founder and Principal Partner of Niyati Technologies, the company behind Safetymint.
He’s a dedicated advocate for workplace safety. Ramesh firmly believes that every individual deserves to return home safely after a day’s work. Safetymint, the innovative safety management software, emerged from this conviction. It’s a platform designed to streamline safety management, empower safety professionals, and enhance safety in workplaces.
Through his blog, Ramesh shares insights, best practices, and innovative solutions for workplace safety. Visit his social media profiles to follow him for regular updates.