The Permit to Work System, often referred to as PTW, is a
critical operational procedure employed by organizations to
grant documented permission for tasks deemed hazardous or
non-routine. This guide provides an in-depth understanding of
the Permit to Work System, the various types of work permits,
the benefits of digitization, and effective implementation
strategies.
What is a Permit to Work system?
A Permit to Work System or PTW is a standard operational procedure used by organizations to issue documented permission to perform tasks that are considered hazardous or non-routine. A permit to work form consists of specific instructions of the nature of the job, the time and place along with adequate information of critical safety procedures to follow.
A valid permit to work document, whether paper-based or digital, should include the following key components to ensure safety, compliance, and clear communication:
Authorization: Work should only begin after obtaining approvals from designated personnel at various stages of permit management. This ensures that all safety measures are reviewed and validated.
Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the responsibilities of all individuals involved in the task, from workers and supervisors to safety officers and permit issuers. Everyone should understand their role in ensuring a safe work environment.

Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment: A thorough assessment of potential hazards must be conducted, detailing risks associated with the task and the necessary control measures. This may include site audits, equipment checks, and personnel training to mitigate risks effectively.
Task Scope & Description: Provide precise details about the work to be carried out, including its purpose, location, expected duration, and step-by-step instructions. Defining the scope helps prevent unauthorized deviations and ensures safety requirements are met.
Communication & Emergency Protocols: Establish clear communication channels to relay safety procedures, emergency protocols, and key contacts in case of incidents. Workers must be informed about emergency response steps, including how to report issues and manage unexpected risks.
Monitoring & Compliance: Regular safety checks and monitoring processes should be in place to ensure adherence to permit conditions throughout the job. Supervisors should conduct periodic inspections to verify compliance and address any deviations immediately.
Status Tracking & Documentation: A structured system should be used to record and track permit statuses—whether open, closed, canceled, revoked, or reissued. Maintaining accurate documentation helps with audits, compliance, and post-task evaluations to confirm that the work site has been restored to a safe condition.
Permit Closure: Once the task is completed or suspended, the permit should be formally closed with confirmation that all safety protocols were followed, the site was restored, and any remaining hazards were addressed. Proper closure prevents future liabilities and ensures a smooth transition to normal operations.
Why use a Permit to Work System?
A permit to work system provides an easy way for organizations to keep a constant eye on work-flows using a well-documented system to streamline operations and control safety outcomes.
Without a work permit, you unintentionally put yourself and those around you in danger. For example: Imagine being stuck or asphyxiated in a confined space with no one knowing you’re actually there or operating machinery without enough practice or training.
The Permit to Work System offers several compelling advantages:
Enhanced Safety
Ensures that personnel are adequately equipped with the right Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), trained in safe working procedures, and informed about potential risks before commencing their duties.
Increased Accountability
By granting permits, organizations shift responsibility for any incidents or near misses to themselves, emphasizing safety as a top priority.

Improved Analysis
Maintaining records and data compilation provides insights into incident regulation, accounting for human error probabilities, and facilitating investment in better safety equipment and operational procedures.

Who Manages a PTW System?
Effective management of a Permit to Work (PTW) system requires the involvement of various key personnel. This section outlines the primary roles involved in overseeing and implementing the PTW process.
Permit Originator: The individual who initiates the permit request, detailing the task and its requirements.
Permit Issuer: The authority responsible for reviewing and approving the permit request, ensuring all safety protocols are met.
Permit User: The worker or team assigned to carry out the task as specified in the permit.
Site Checker: The person tasked with inspecting the worksite to verify that it meets all safety conditions before work begins.
Supervisor: The individual overseeing the entire process, ensuring compliance with the permit's conditions and managing any issues that arise during the task.
Safety Officer: A dedicated role focused on monitoring safety protocols and ensuring all safety measures are strictly adhered to throughout the task.
Escalation Reviewer: A designated authority who can override the reviewer in case of unavailability or disputes, ensuring continuous workflow and safety compliance.
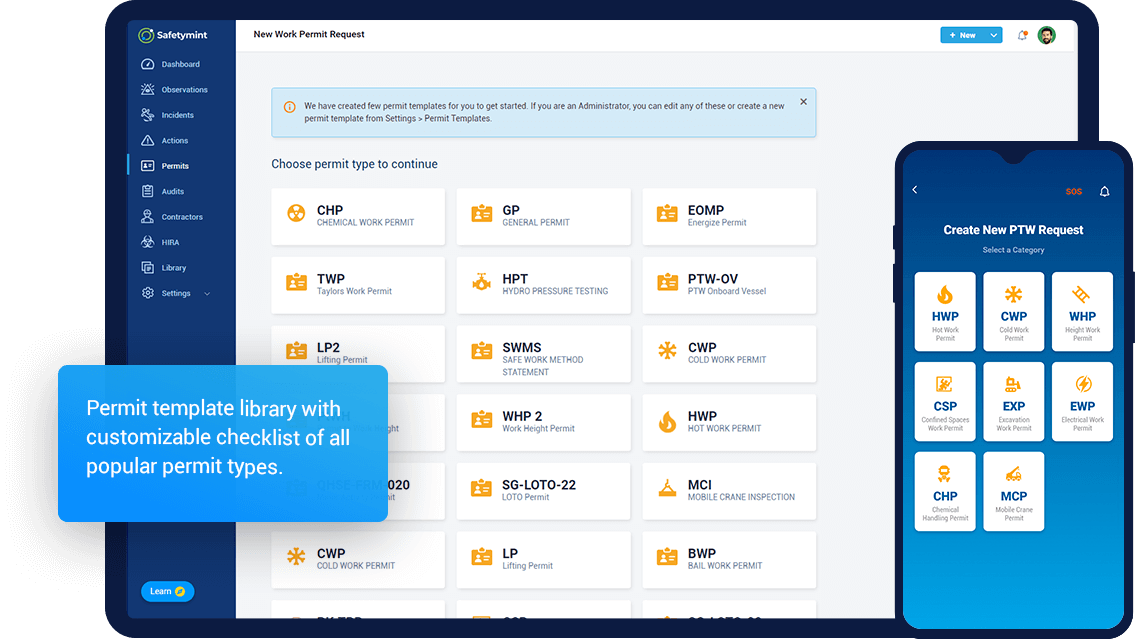
What are the types of Work Permits?
There are seven main types of work permits: Hot Work Permits, Cold Work Permits, Confined Spaces Work Permits, Chemical Work Permits, Height Work Permit, and Excavation Permit. Each work permit is categorized depending on the nature of the job and the hazard involved in it.

Do’s and Don’ts of Permit to Work
Adhering to best practices and avoiding common pitfalls is crucial for the success of any Permit to Work system. This section outlines essential do’s and don’ts to help ensure a safe, efficient, and compliant work environment.
Do’s:
1. Conduct Comprehensive Training: Ensure all personnel involved are adequately trained in the Permit to Work system and understand their roles and responsibilities.
2. Perform Thorough Risk Assessments: Evaluate all potential hazards associated with the task and document preventive measures to mitigate risks.
3. Verify Authorization and Approvals: Obtain necessary approvals from designated personnel at various stages of the permit process to ensure all safety protocols are followed.
4. Use Digital Templates and Forms: Utilize digital permit templates to streamline the issuance and management of permits, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
5. Ensure Clear Communication: Maintain open lines of communication between all parties involved, including contractors, workers, and management, to ensure everyone is aware of permit status and safety requirements.
6. Maintain Updated Records: Keep accurate and up-to-date records of all permits, including their status, any incidents, and lessons learned for future reference.
7. Regularly Review and Update Procedures: Continuously review and update your Permit to Work procedures to incorporate new safety standards, technologies, and best practices.
Don’ts:
1. Skip Risk Assessments: Never bypass the risk assessment process, as it is crucial for identifying and mitigating potential hazards.
2. Ignore Unauthorized Work: Do not allow any work to commence without a valid, approved permit to work. Unauthorized tasks increase the risk of accidents and non-compliance.
3. Neglect Training: Avoid assuming that workers are familiar with the permit process. Always provide comprehensive training and refresher courses.
4. Delay Communication: Do not delay in communicating any changes or updates related to the permit. Timely information ensures everyone is on the same page and can react promptly to any issues.
5. Overlook Documentation: Never overlook the importance of detailed documentation. Incomplete records can lead to misunderstandings and missed safety protocols.
6. Forget About PPE: Do not permit work to start without ensuring that all necessary Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is available and properly used.
7. Disregard Permit Closure: Always ensure permits are properly closed out after the task is completed. This includes verifying that the work was conducted safely and all safety measures were adhered to.
Permit to Work Digitization
Digitization of Permit to work system helps to remove the tiresome Excel-based or paper-work processes which are normally associated with a manual PTW system. With an electronic permit system, you can optimize the whole process to create a system that is always connected, easy to use, highly collaborative with increased accessibility and control of permits
An electronic permit system offers several advantages, including:
Efficiency: Instant issuance of permits with the necessary authorizations.
Real-time Information: Immediate transmission of permit details to authorized personnel.
Centralized Database: All permit activities, from issuance to closure, can be accessed remotely via any connected device.
Performance Monitoring: Gain valuable insights into the progress of operations.
Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitates communication between management and on-site personnel for instant safety permit status updates.
Automation: Smart automation technology ensures permits are issued or rejected only when all criteria are met and safety procedures are in place.
Notifications: Receive instant alerts and notifications throughout the management chain regarding permit activities, requests, and escalations.
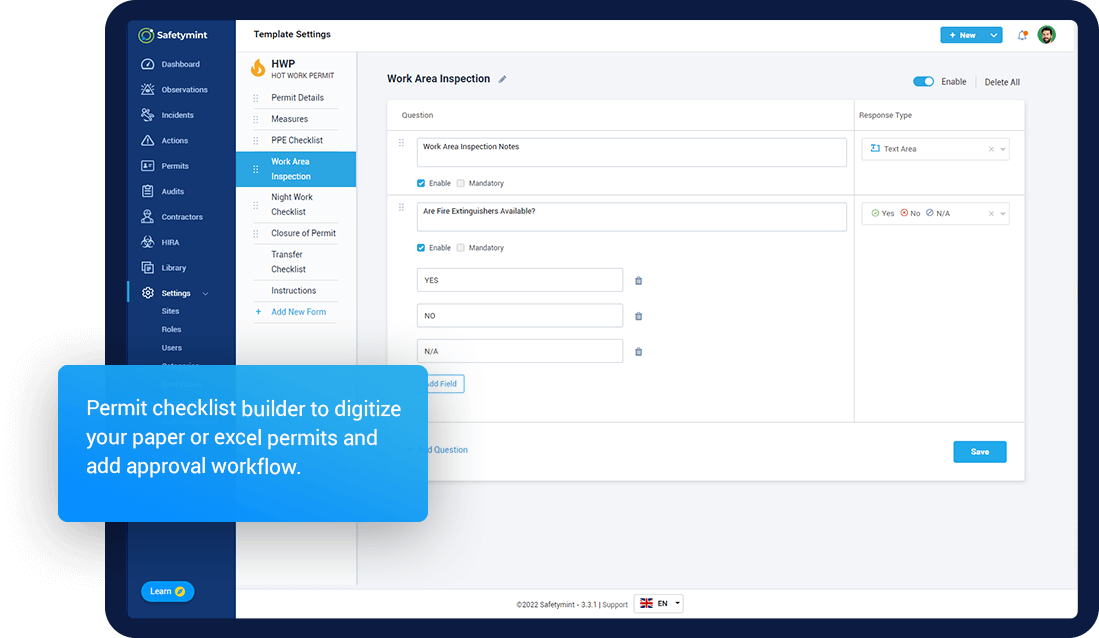
PTW Checklist
A Permit to Work checklist is a comprehensive documentation of everything associated with the work permit to be issued. The checklist template has to cover all the aspects of a work permit including the work related details, safety checks to be followed, worker profiles, emergency protocols, authorizations, duration of work etc.
Let's explore some of the elements essential for a permit checklist:
Complete Credentials & Authorizations
Names, designations, and signatures from the originator, permit user, issuing authority, site checker and other designated authorities.
Permit Title and Reference Number
To give a clear identification to the permit to work form to ensure that permits can be easily stored and retrieved.
Job Location and Timing
Job Location and Timing: Names, designations, and signatures from the originator, permit user, issuing authority, site checker and other designated authorities.
Plant Identification
This will help in pinpointing the exact location of the plant where the task is to be performed.
Description of work
A complete summary of the task to be performed with procedures to follow, the scope of work and limitations.
Hazard Identification
A complete summary of hazards that you may face during the job from residual, ergonomic, physical, radiation and much more.
Precautionary Steps
Safety measures to take to avoid any hazardous circumstances that may arise during the job.
PPE
A list of the safety gear needed while performing the assigned task. Safety equipment includes gloves, respiratory mask, safety helmets, footwear, harness and much more depending on the job.
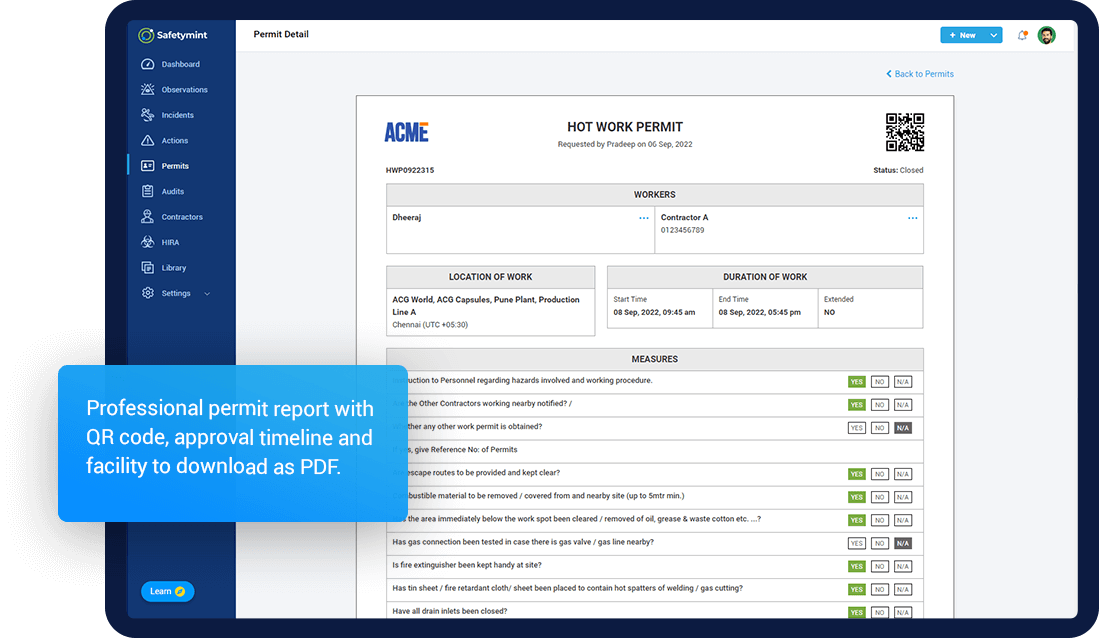
Permit Sign Off
The final part of the permit to work system where you will have to mention if the work assigned is completed or incomplete.
Visit our free permit templates section, where you'll find the following checklists:
Implementing a Permit to Work System
Success in implementing a Permit to Work System relies on several critical factors:
- Emphasizing the importance of a permit to work system and when it should be used to everyone involved in your organization.
- Provide adequate and comprehensive training program to your staff, no matter how good your permit to work system is.
- Make sure that no job starts without a validated permit to work.
- Make sure that all required authorizations are granted before the start of the task.
- Make sure that the completed permit is stored and managed properly
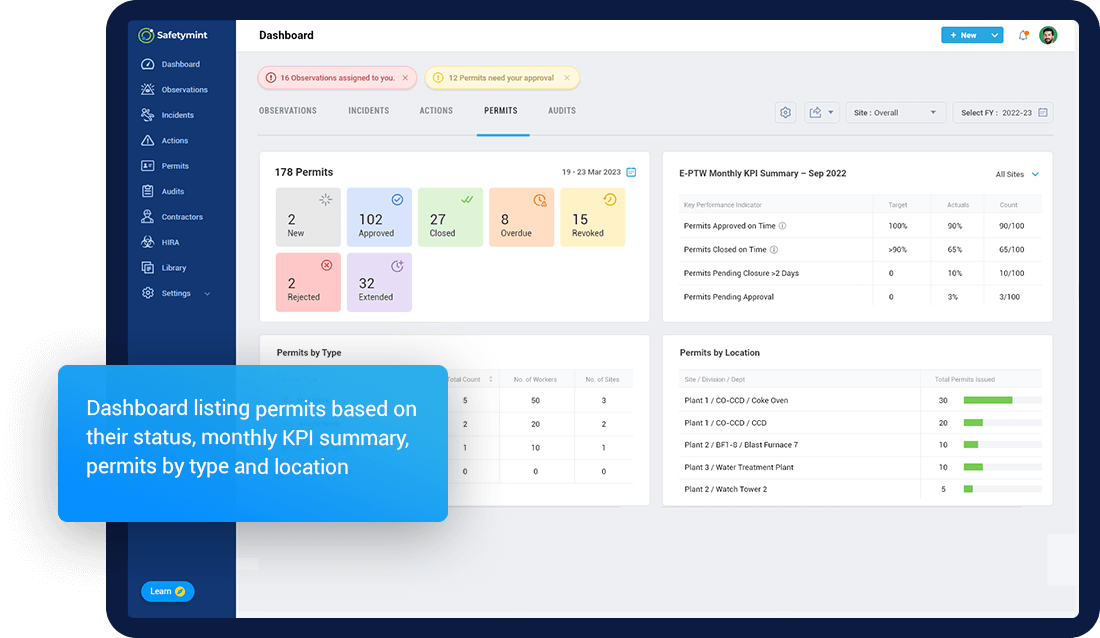
Safetymint Permit to Work System
As an end-to-end permit management system, Safetymint is well positioned to handle all your work permit activities – including JSA, HIRA and contractor management. The software is used across industries – from oil & gas to construction, manufacturing and pharma. Some of the key features include:
- Easy permit template builder
- Robust dashboard
- Map plotting
- Customizable workflow
- Contractor management system
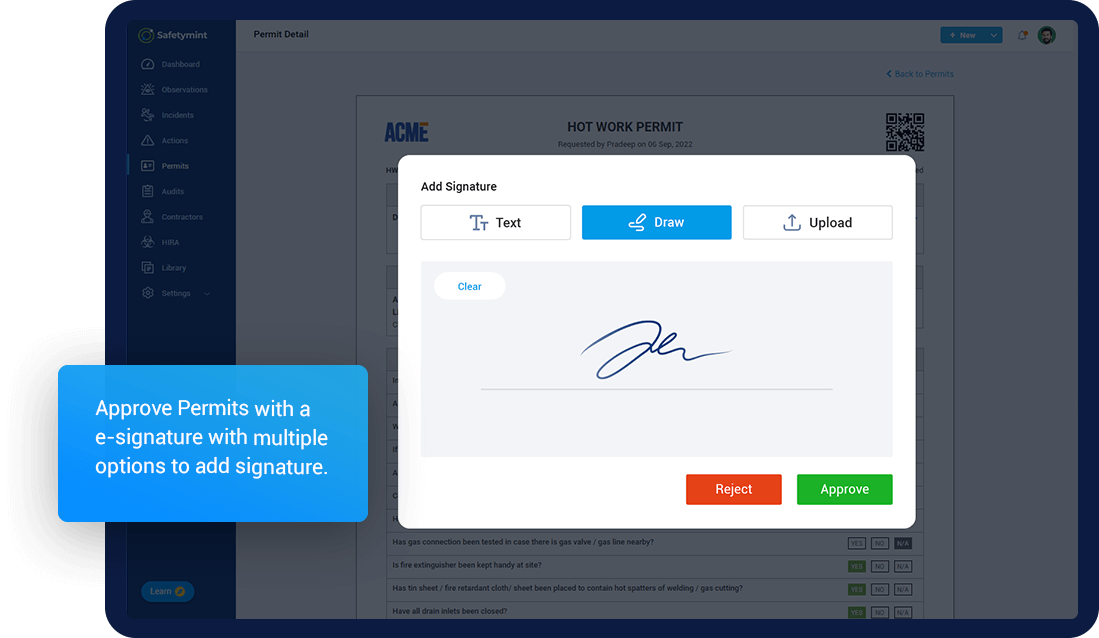
- Digital signature
- Access via web browser or mobile apps
- Customizable to fit your requirements
The permit application has a clean and intuitive interface design that requires minimal training: